Wumpus World Game
Hunt the Wumpus is a text-based adventure game developed by Gregory Yob in 1973. Other sources, however, such as the book The World of Scary Video Games, claim that the game lacks elements needed for a 'horror' game, as the. Hunt the Wumpus is an early computer game, based on a simple hide and seek format featuring a mysterious monster (the Wumpus) that lurks deep inside a network of rooms. It was originally a text-based game written in BASIC. It has since been ported to various programming languages and platforms including graphical versions.
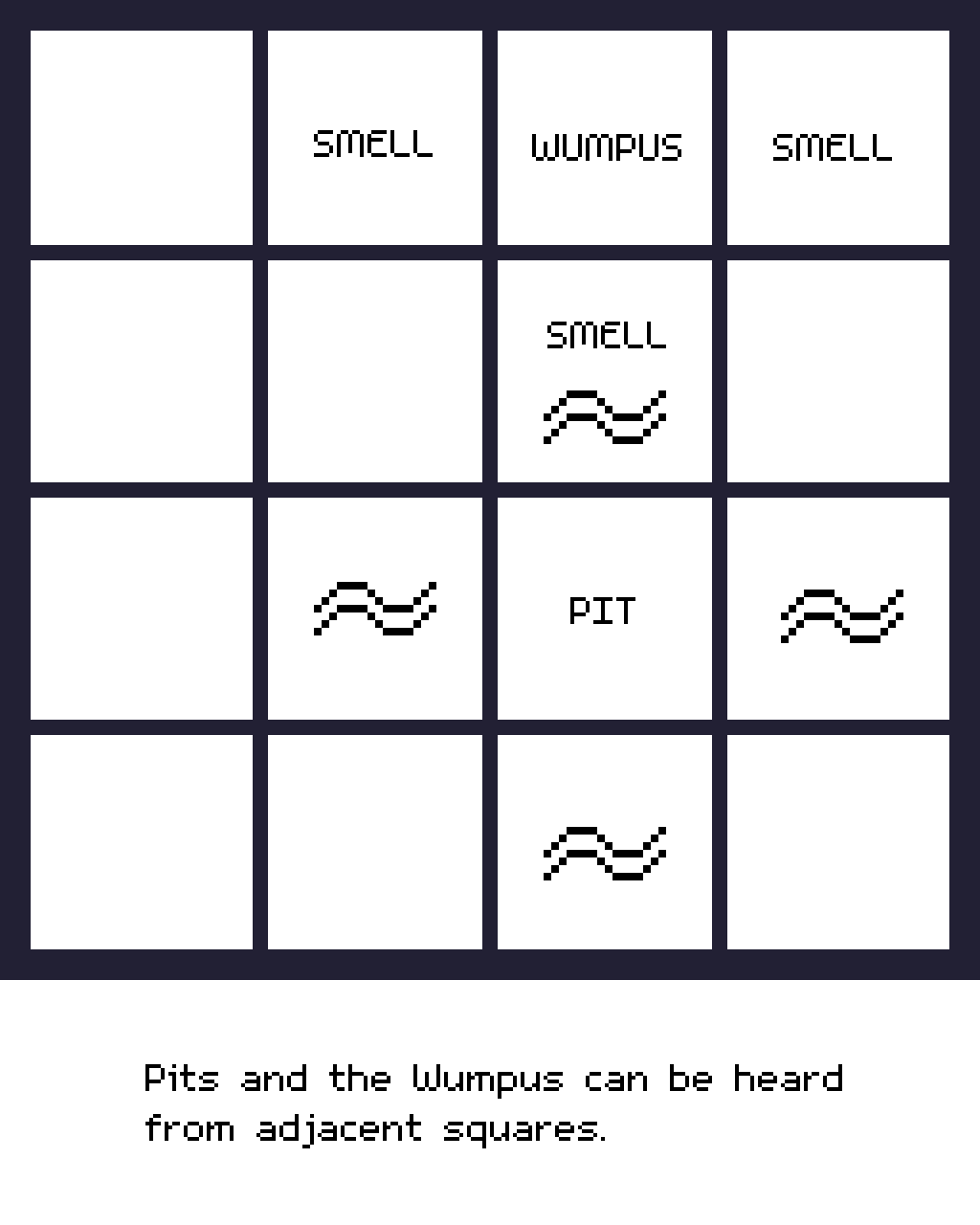
Knowledge-base for Wumpus worldAs in the previous topic we have learned about the wumpus world and how a knowledge-based agent evolves the world. Now in this topic, we will create a knowledge base for the wumpus world, and will derive some proves for the Wumpus-world using propositional logic.The agent starts visiting from first square 1, 1, and we already know that this room is safe for the agent.
To build a knowledge base for wumpus world, we will use some rules and atomic propositions. We need symbol i, j for each location in the wumpus world, where i is for the location of rows, and j for column location.
Atomic proposition variable for Wumpus world:. Let P i,j be true if there is a Pit in the room i, j. Let B i,j be true if agent perceivesbreeze in i, j, (dead or alive). Let W i,j be true if there is wumpus in the squarei, j.
Let S i,j be true if agent perceives stench in the square i, j. Let V i,j be true if that squarei, j is visited. Let G i,j be true if there is gold (and glitter) in the square i, j. Let OK i,j be true if the room is safe.Note: For a 4.
4 square board, there will be 7.4.4= 122 propositional variables. Some Propositional Rules for the wumpus world: Note: lack of variables gives us similar rules for each cell.
